OSI Layer Model
Ø Open System
Interconnection (OSI) model is
a conceptual model that covers all aspects of network communications.
Ø This model characterizes and standardizes the
internal functions of a communications system by partitioning it into abstraction
layers.
Ø This is a model that allows any two different
systems to communicate regardless of their underlying architecture (hardware or
software).
Benefits of OSI
Model
v Reduces complexity.
v Standardizes interfaces.
v Facilitate modular engineering.
v Ensure interoperable technology.
v Simplify teaching and learning.
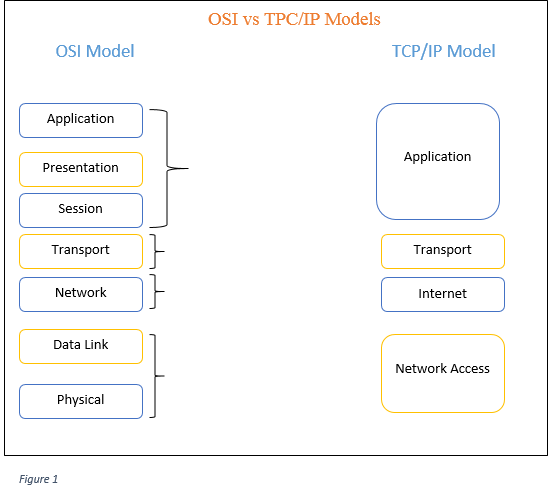
OSI vs TPC/IP Models
Ø Physical Layer
The
physical layer coordinates the functions required to transmit a bit stream over
a physical medium. It also defines the procedures and functions that physical
devices and interfaces have to perform for transmission occur. The physical
layer is responsible for transmitting individual bits from one node to the
next.
Ø Data Link Layer
Provides
connectivity and path selection between two hosts. The data link layer is
responsible for transmitting frames from one node to the next.
Ø Network Layer
Provide
Reliable Transfer of data across media. The network layer is responsible for
the delivery of packets from the original source to the final destination.
Ø Transport Layer
Concerned
with Transportation issues between hosts. Establish. Maintain, terminate
virtual circuits. The transport layer is responsible for delivery of a message
from one process to another.
Ø Session Layer
Establishes,
manages and terminates sessions between applications.
Ø Presentation Layer
Ensure
data is readable by receiving system. Consider about format of data and
structure of data.
Ø Application Layer
Provides
network services to application processes. The application layer is responsible
for providing services to the user.
Bandwidth
In
computer networks, bandwidth is often used as a synonym for data transfer rate
- the amount of data that can be carried from one point to another in a given
time period (usually a second).
Ø Important of bandwidth
v Bandwidth
is limited by physics and technology.
v Bandwidth
is not free.
v Bandwidth
requirements are growing at a rapid rate.
v Bandwidth
is critical for network performance.
Ø Bandwidth Measurement
 |
Network Layer
The
Network layer is responsible for the source-to-destination delivery of a packet
possible across multiple networks. If two systems are connected to the same
link, there is usually no need for a network layer. However, if the two systems
are attached to different networks, there is often a need for the network layer
to accomplish source-to-destination delivery.